
Introduction
Infertility Introduction
What An Infertility Evaluation Involves

Testing For Infertility

Treatment Options
Infertility
The world’s leading medical organizations generally define infertility as a couple not being able to get pregnant after one year or more of unprotected sex. About 1 in 6 people globally experience infertility according to a report by the World Health Organization, with the disease of the female or male reproductive system not discriminating based on geographic location or income level.
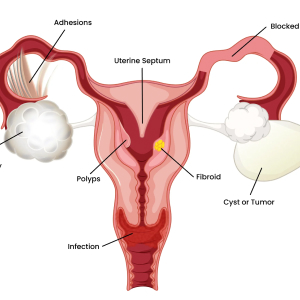
Causes of Infertility:
Infertility may be caused by more than one factor, with some being easy to treat while others are more complex. The causing factor(s) may result to the female or male, with fertility capability declining with age. Female causes for infertility may include the following:
- Endometriosis
- Ovaries not producing enough eggs at the right time
- Abnormal hormone levels
- Uterus conditions
- Scarring or blockages in the cervix or tubes
- Lifestyle factors such as obesity, poor nutrition, anorexia or tobacco, marijuana or alcohol use
- Male causes for infertility may include the following:
- Low sperm count or poor sperm health
- Abnormal hormone levels
- Infection or scarring from a sexually transmitted disease
- Blockages, damage or an injury to the reproductive organs
If you have been afflicted by infertility, you are not alone. The friendly and knowledgeable team at GoFertility in St. Louis is here to compassionately help in your journey to having a baby and attaining parenthood.
GoFertility (also known as CRMRS) has helped hundreds of couples successfully get pregnant, and you can read their success stories here. Since our opening in 2011, we have beaten the national pregnancy rate per embryo transfer every year. We were named one of the top-50 best fertility clinics in the U.S. by Newsweek in 2023 — one of just two clinics in Missouri to earn this distinction. (#Success Stories)

Testing:
The decision to begin testing depends on a number of factors. They include your age and your partner’s age, as well as how long you have been trying to get pregnant. You and your partner will receive care as a couple. Testing involves an evaluation as follows:
- Physical exam of both partners
- Medical history
- Semen analysis
- Ovulation check
- Tests to check for a normal uterus and open fallopian tubes,
- Discussion about how often and when you have sex
The basic workup of an infertility evaluation can be finished with in 14 days from the start of the menstrual cycle. Please discuss with the Center about the costs involved and find out whether they are covered by your insurance.
Female ovulation assessments may include at-home tests — such as a urine test or basal body temperature test — or blood samples to evaluate hormone levels. Additional tests may need to be conducted, such as:
- Transvaginal ultrasound or sonohysterogram, which checks the ovaries and uterus
- Hysteroscopy, in which a telescope-like device helps the doctor examine the inside of the cervix and uterus
- Hysterosalpingography (HSG), an X-ray showing the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes
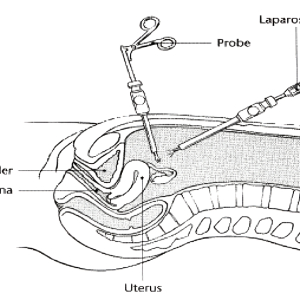
- Laparoscopy, in which a small video camera is inserted through a tiny surgical incision (5 millimeters) through the belly button to enable the doctor to view the reproductive organs with great detail
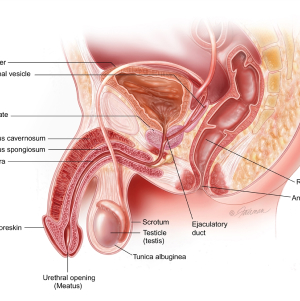
Basic Workup for the Man:
A general physical examination and semen analysis is a key part of the basic workup for a man. Semen analysis may need to be done more than once. The semen sample is obtained by masturbation. Sometimes it can be obtained at home but usually it is obtained in our lab. Our staff will give you instructions. Our lab will study the sperm using specific criteria for:
- Number
- Shape
- Movement
- Signs of infection
- Morphology
Based on the initial evaluation, further testing may be required in the Center, including genetic and chromosomal testing. It is recommended that the man abstain from ejaculation 3- 5 days before the semen test.
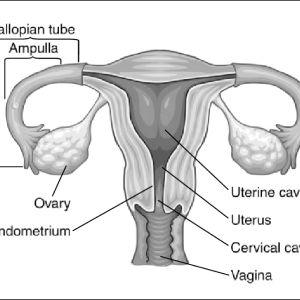
Procedures:
Procedures are used to look at a woman’s reproductive organs. They check if the uterus is normal and the fallopian tubes are open. The tests you have depend on your factors and symptoms.

Trans-vaginal ultrasound/Sono-hysterogram. This test checks the ovaries and uterus by using sound waves to produce pictures of pelvic organs. First, a device (a transducer) shaped like a wand is lubricated and inserted into the vagina. A machine displays an image of the organs. In sono-hysterogram, a fine catheter is introduced into the uterus and the uterine cavity is instilled with saline solution, followed by ultrasound scan. This helps to visualize the cavity of the uterus. This test is commonly done on any day between day 2 and day 7 of your menstrual cycle.
Since the Center does not know when you start your period, it is the patient’s responsibility to call and schedule these appointments. Please call the Center to make an appointment or click here and schedule appointment through the secure patient portal.
Hysterosalpingography (HSG). This test is an X- ray that shows the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes. In most cases, it is done right after a menstrual period. A small amount of dye is placed in the uterus through a thin tube inserted through the cervix. An X-ray is then taken. The dye outlines the inside of the uterus and fallopian tubes. If it spills from the tubes, it shows that the tubes are open. This test is commonly done on any day between day 10 and day 14 of your menstrual cycle. Please call the Center to schedule this appointment.
Since the Center does not know when you start your period, it is the patient’s responsibility to call and schedule these appointments. Please call the Center to make an appointment or click here and schedule appointment through the secure patient portal.
Hysteroscopy. This procedure lets the doctor look inside the uterus. A thin telescope-like device, called a hysteroscope, is placed through the cervix. The uterus may be filled with liquid to reveal more information. During this procedure, the doctor can correct minor problems or get a sample of tissue to study. The doctor also may decide other procedures are needed. This test is commonly done on any day between day 7 and day 14 of your menstrual cycle.
Laparoscopy. This procedure lets the doctor view the tubes, ovaries, and the outside of the uterus. It is usually performed in the hospital under anesthesia. A small telescope-like device, called a laparoscope, is inserted through a small cut (about 1 inch or less) at the lower edge of the navel. Fluid is placed in the uterus to see if it spills from the ends of the tubes. This shows if the tubes are open or blocked. The doctor also can look for pelvic problems, such as endometriosis or scar tissue.
Post Testing Consultation:
After your basic testing as detailed above is completed, you and your partner will have a post testing consultation with the staff and the doctor. At this appointment, the results of all the tests performed are discussed in detail and a treatment plan is adopted. This may include just waiting for natural pregnancy, ovulation induction with clomid and or injectable medications, intrauterine insemination (IUI) or in-vitro fertilization (IVF).
Men with very low sperm count may opt for ICSI procedure with IVF. Once a treatment plan is finalized a protocol is written up with dates and time of all appointments, when to take the medications, etc.
Treatment:
Infertility can be treated in many ways, including lifestyle changes, medication, surgery, and assisted reproductive technologies. After your initial evaluation at the Center, we will discuss with you the appropriate treatment options based on your medical condition, age, personal desires, religious beliefs and financial situation. The common Assisted Reproductive Technologies are:
- Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
- In-vitro fertilization and Embryo transfer (IVF-ET)
- Intra cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI)
- Microsurgical sperm extraction from the testes or epidydimis (MESA/TESA) and ICSI
- Donor Oocyte program
- Donor Embryo program
- Gestational surrogacy program
The choice depends on the cause. After your evaluation, please discuss with the staff at the Center about the best treatment options for you and your partner. You also may choose adoption, foster parenting or other alternatives. Supporting you in whichever decision you make is our priority.